FAQs
The Standard Risk Measure is based on industry standards to allow super members to compare investment options that are expected to deliver a similar number of negative annual returns over any 20-year period. Each investment option provided by AMP Super includes a Standard Risk Measure.
It’s not a complete assessment of investment risk and members should still make sure they are comfortable with the risks and potential losses associated with their chosen investments.
You can switch between investment options at any time, and there's no switching fee for doing so, however transaction costs may be incurred.
You may change your investment options at any time by securely accessing My AMP, your online account. Before you decide to switch, we recommend you speak to a financial adviser. Please read your investment guide for more information about switching, available in My AMP.
An auto-rebalancing facility means we’ll keep your funds invested according to your nominated investment profile. You can choose to have your account rebalanced either quarterly, half yearly or yearly.
You can learn more in your super account’s investment guide, available in My AMP.
Diversification in simple terms means not putting all your eggs in one basket. It's a way to spread risk by investing in different markets as these can rise and fall at different times. This can also include using a range of different investment managers as well as different investment styles.
Growth assets (including shares, property and infrastructure) usually have a higher level of volatility than defensive assets and their asset values can change, sometimes markedly, from day to day. However, they have the potential for higher returns, over the longer term, than defensive assets.
Defensive assets (including cash and fixed interest) are less volatile than growth assets, however their overall return potential is also lower.
Gearing is the process of borrowing money to purchase assets. Gearing can magnify an investment’s potential gains or losses. There is also a risk the assets will be exposed to increases in interest rates, which increases the borrowing cost and may reduce the potential returns of the investment.
Liquidity means that investors can easily convert their investments into cash in both good and bad times. Having cash available means an investor has the flexibility to use that cash for things like portfolio redemptions and asset allocation changes.
Your money has reduced purchasing power over time due to inflation.
For example, 30 years ago, shopping with $15 may have allowed you to purchase a larger quantity of goods and services than you can today. Also, 30 years from now, you will likely be able to afford fewer goods and services compared to today with your $15.
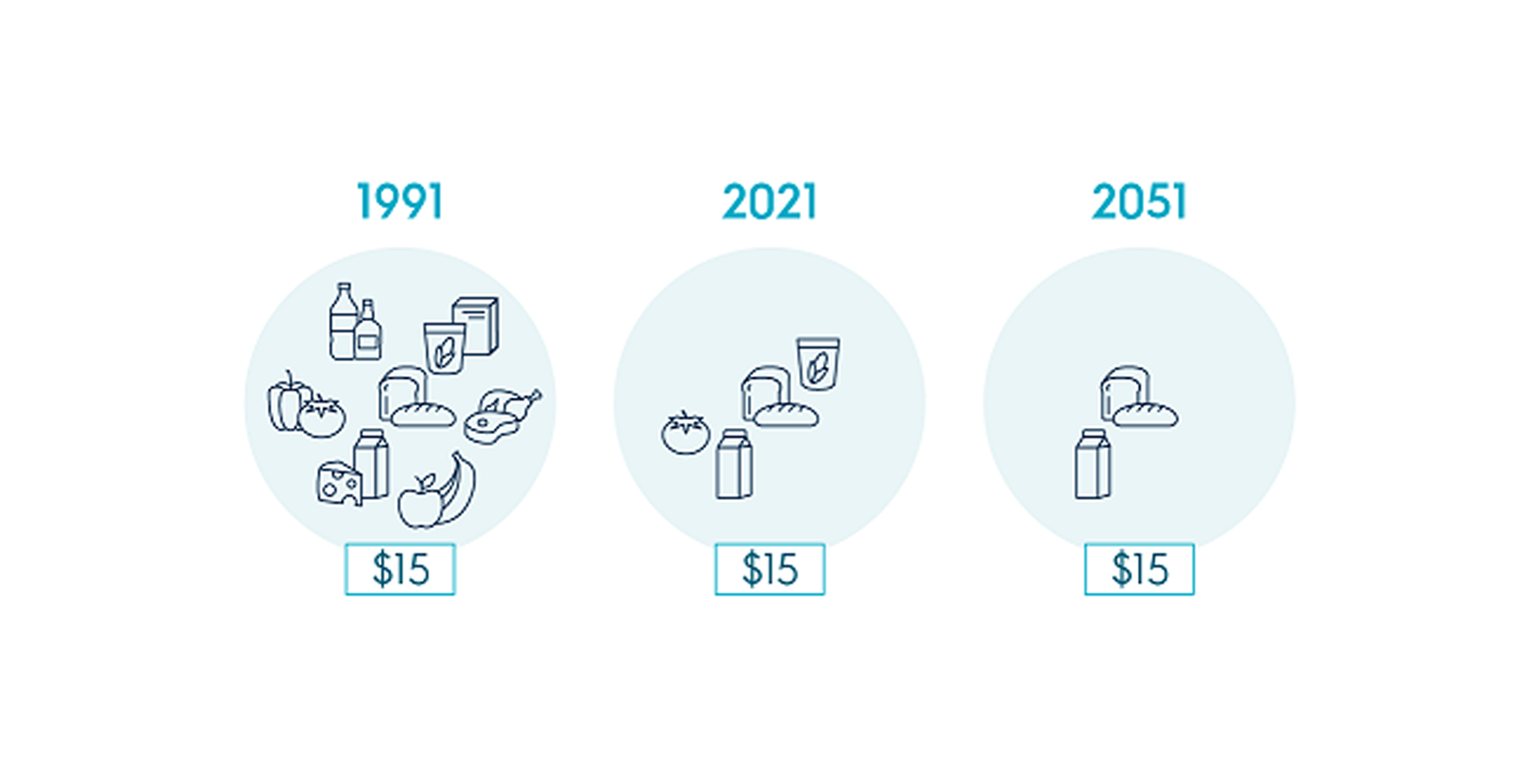
To maintain your purchasing power, your investment return needs to increase by at least the rate of inflation. Otherwise, the real value or purchasing power of your investment will decline.
You should consider this when choosing your investment options. Depending on the time until you retire, you may need significantly more wealth to purchase the same level of goods and services.
Keep in mind that investments which aim to exceed the rate of inflation may be associated with other risks due to the exposure to growth assets, including shares, property and infrastructure. Refer to the Investment risk and returns section in your Investment guide for more information about the risk and return characteristics of growth assets.






